 gh
gh 2v22/2 +
2v22/2 + 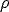 2gh
2gh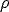 1v12/2 +
1v12/2 + 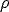 1gh
1ghYou have 2 hours to answer 8 questions on this exam. Please answer each question only on the sheet provided for this problem, using the back if necessary. Please write the name and the last 4 digits of your SS# on each sheet at the top of the page.
You must indicate the reasoning and show all the steps.
If you are unable to obtain the answer to part of a problem and you need the answer to solve the subsequent parts, use an appropriate symbol for the answer to the previous part and solve in terms of that symbol.
The following may be useful:
| g | = 10m/s2 | ||
| v2 | = v 02 + 2as | ||
| x | = x0 + v0t + at2/2 | ||
| ac | = v2/R | ||
| PV | = nRT | ||
| R | = 8.31J/mol . K | ||
| NA | = 6.022 × 1023mol-1 | ||
 | = I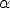 | ||
| P2 | = P1 + 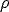 gh gh | ||
P2 + 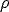 2v22/2 + 2v22/2 + 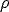 2gh
2gh | = P1 + 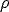 1v12/2 + 1v12/2 + 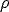 1gh
1gh |
1. (5 points) The free body diagram in the drawing shows the forces acting on a thin rod.
The three forces are drawn to scale and lie in the plane of the paper. Are these forces
sufficient to keep the rod in equilibrium, or are additional forces necessary? Explain.
2. (5 points) A glass beaker, filled to the brim with water, is resting on a scale. A block of wood is placed in the water, causing some of it to spill over. The water that spills is wiped away, and the beaker is still filled to the brim. How do the initial and final readings on the scale compare? Explain your answer.
3. (10 points) Three jumper leaves the ground at angle of 30o, 45o, 60o, and each with a takeoff speed 8m/s. For each,
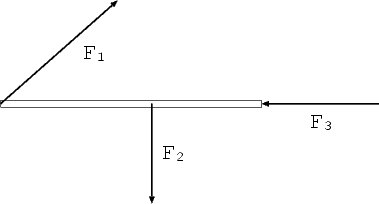
4. (20 points) An external force is applied on a block with an angle 37o as shown in the figure. The magnitude of the force is 50N. The mass of the block is 10kg. There is friction between the ground and the block.
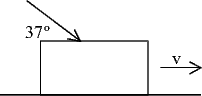
5. (15 points) The ropes and the pulley are massless. A person is pulling two blocks together with a force 80N.
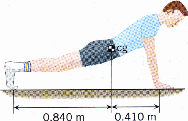
6. (10 points) The drawing shows a person whose weight is W=585N doing pushups. Find the normal forces exerted by the floor on each hand and each foot, assuming that the person holds this position. “cg” denotes the center of gravity of the person.
7. (15 points) An object of mass m=0.200kg attached to a spring is vibrating on a horizontal frictionless surface. The spring has a spring constant k=500N/m. It is stretched initially for x0 = 4.5cm and then released from rest.
 and period T of this SHM.
and period T of this SHM.
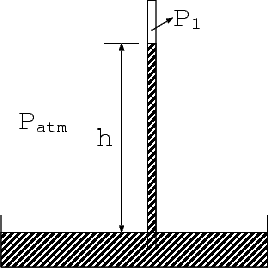
8. (20 points) A mercury barometer is shown in the following figure. The atmospheric
pressure can be determined from the height h of the mercury in the tube. The mass
density of mercury is 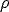 = 13.6 × 103kg/m3. The standard atmospheric pressure is
Patm = 1.013 × 105Pa. No air is enclosed inside the tube except for a negligible amount of
mercury vapor hence the pressure (P1) inside the tube can be regarded as zero.
= 13.6 × 103kg/m3. The standard atmospheric pressure is
Patm = 1.013 × 105Pa. No air is enclosed inside the tube except for a negligible amount of
mercury vapor hence the pressure (P1) inside the tube can be regarded as zero.